What is CI/CD?
What Are No Code Tools?
In traditional development, all aspects of an application are created through the creation of source code. This approach offers the most control and flexibility, meaning its ideal for complex, large scale projects that need specific functionality.
Traditional development often requires complex systems, databases, machine learning apps and mobile games that require exact performance, security, or scalability requirements. The software produced can really do almost anything the company wants as all features are coded, but projects often take months to deploy.
Continuous Delivery vs Continuous Deployment
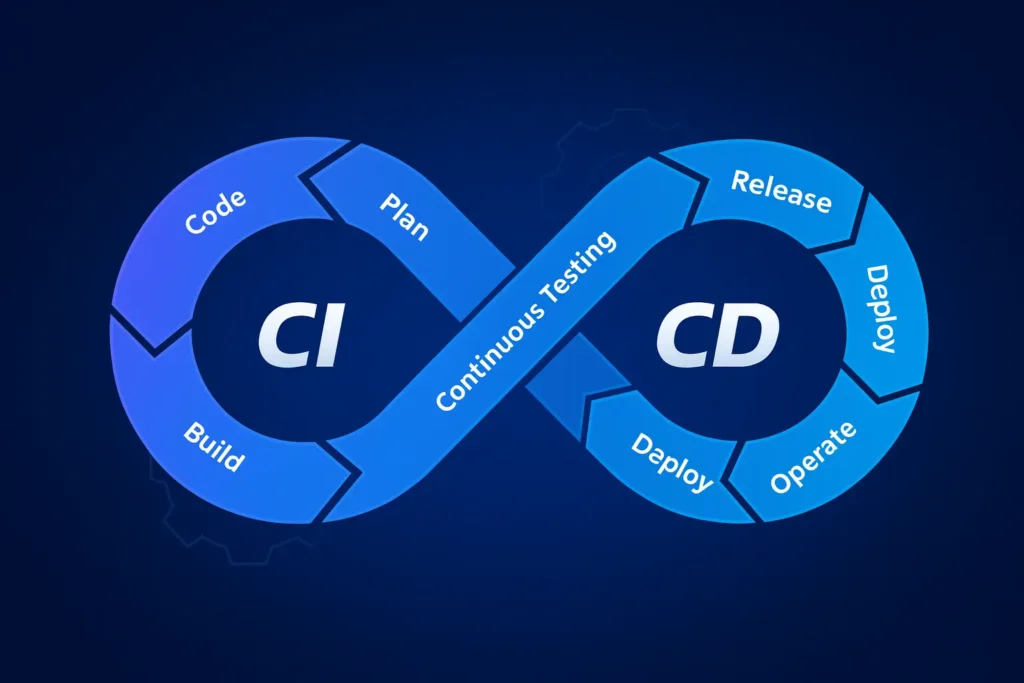
Continuous Integration (CI):Developer merge their code in shared repository. Every time developer pushes code, automated system build this code and test it.
This automated test, build and verification help to catch the problem early before they become dig problems.
Continuous Deployment (CD):Once the code passes all checks, it is deployed to the production environment automatically. This eliminates the delays of releases and ensures that the new features and updates reach users faster, and users always get the latest version.
CI/CD Tools:
- For GitHub projects → GitHub Actions or Travis CI
- For enterprise workflows → Azure DevOps, TeamCity, or Bamboo
- For cloud-native teams → CircleCI or Spinnaker
- For full DevOps lifecycle → GitLab CI/CD
Why is CI/CD Important?
Speed: Teams can release updates daily instead of weekly or monthly.
Quality: Automated testing reduces human error and prevents broken features from going live.
Collaboration: Multiple developers can work together without breaking the main codebase..
Reliability: If something fails, rollbacks are easy, and issues can be fixed quickly.
Customer Satisfaction: Users get improvements and new features without long waits.
CI/CD Pipeline Workflow

Code Commit: Developers push their changes to the version control system like GitHub, GitLab.
Build: The system compiles the code and prepares it for execution.
Test: Automated tests are run to verify functionality.
Deploy: If the code passes the tests, it is deployed to a staging or production environment.
Production: Users can now access the updated software.
Example: A small feature’s journey: You add a new login button:
- Commit code → pipeline triggers build and unit tests.
- Integration tests run against a test database.
- If tests pass, the artifact deployed to staging. Manual QA or automated acceptance runs.
If all is clear, the change promoted to the production environment. Users see the button minutes or hours after the initial commit
Conclusion:
CI/CD is less about specific tool and more about a habit by integrating changes frequently. Automate repeatable things and get feedback fast for improvement. Start with a minimal pipeline that run builds and test on evert commit. Then add deployment stages and security checks. This will help to faster releases that makes teams happier.